
The Overflow Valve Block plays a critical role in hydraulic systems. It regulates fluid pressure, ensuring optimal performance. According to industry reports, improper pressure control can lead to system failures, causing significant downtime. This highlights the importance of a well-functioning Overflow Valve Block.
In a hydraulic system, the Overflow Valve Block prevents excess pressure build-up. It acts as a safety mechanism, protecting equipment from damage. Data from Fluid Power Journal shows that equipment failures due to pressure issues account for up to 30% of maintenance costs. This statistic underscores the need for reliable overflow protection.
However, many systems still operate with outdated valve blocks. This creates potential vulnerabilities. Regular maintenance and updates to the Overflow Valve Block are essential to prolong system life. The lack of awareness regarding this component often leads to overlooked issues. Ensuring extensive knowledge in this area can greatly enhance system reliability.
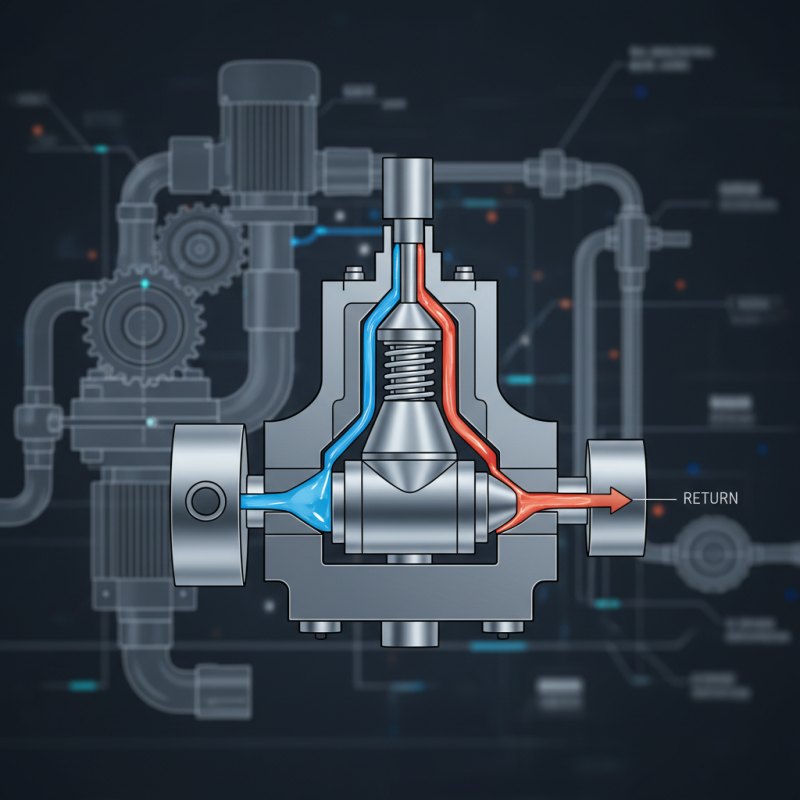
An overflow valve block is a critical component in hydraulic systems. Its primary purpose is to regulate pressure and prevent excess fluid from overwhelming the system. When fluid pressure exceeds a specific limit, the overflow valve opens, allowing fluid to escape. This helps maintain safe operating conditions.
The design of an overflow valve block can vary. Typically, it includes ports for fluid entry and exit, along with a spring-loaded mechanism. This mechanism ensures that the valve opens at the right pressure. When the pressure drops, the valve closes, preventing any further leakage. The efficiency of this system is crucial for machinery performance.
**Tip:** Regular maintenance of the overflow valve block is essential. Check for leaks and proper functioning. A small issue can lead to system failure.
Sometimes, the valve may not open correctly. It can be due to dirt or wear. This can lead to increased pressure, risking damage to the entire system. Observing the pressure regularly can help identify such issues early.
**Tip:** Use quality fluids to minimize contamination. It can significantly extend the life of your overflow valve block. Keeping it clean is more effective than frequent replacements.
This chart illustrates the performance metrics of an overflow valve block, highlighting important parameters such as flow rate, pressure, temperature, and response time. These factors are essential for understanding the efficiency and reliability of the valve in hydraulic systems.
An overflow valve block plays a critical role in hydraulic systems. It ensures that pressure levels remain stable. Key components include the valve body, spring assembly, and sealing element. Each part is essential for functionality. The valve body usually has ports for flow in and out. The spring assembly regulates pressure by pushing against the valve. The sealing element prevents leaks.
Understanding the materials used is vital. Many valve blocks are made from durable metals like steel or aluminum. These materials can handle high-pressure situations. Reports suggest that over 70% of hydraulic failure is due to valve malfunction. A well-maintained overflow valve can significantly reduce operational issues. Proper installation also contributes to overall efficiency.
Maintenance is often overlooked. Regular checks on the spring tension and seals can enhance performance. Neglected components can lead to leaks or even system failure. Industry data shows that replacing worn-out parts can boost system reliability by up to 50%. Operators must remain vigilant. Small changes in pressure can have significant impacts.
| Component | Function | Materials Used | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overflow Valve | Regulates system pressure by allowing fluid to return to the reservoir. | Steel, Aluminum, Brass | Adjustable pressure settings, durable design. |
| Pressure Relief Valve | Prevents overpressurization by venting excess fluid. | Stainless Steel, Plastic | Spring-loaded mechanism, rapid response. |
| Control Block | Coordinates hydraulic pressure and flow between components. | Cast Iron, Aluminum | Compact design, multiple inlet/outlet options. |
| Sensor | Monitors pressure levels and sends signals for adjustments. | Silicon, Carbon Steel | High sensitivity, digital output. |
| Accumulator | Stores hydraulic energy and balances pressure spikes. | Steel, Composite Materials | High capacity, lightweight design. |
An overflow valve block plays a pivotal role in various hydraulic systems. It ensures that excess fluid is redirected safely, preventing damage. The mechanism behind overflow valves is straightforward but critical to system efficiency. When pressure exceeds a predetermined limit, the valve opens. This action allows fluid to bypass the operational circuits, diverting it back to the reservoir.
According to a recent industry report, approximately 30% of hydraulic failures can be traced back to improper pressure management. When these systems do not have effective overflow valves, risks increase significantly. Regular maintenance can mitigate these issues. However, some operators overlook this aspect, leading to catastrophic failures. The consequence can be costly downtime and repairs.
The functionality of these valves hinges on precision. A minor dirt accumulation can cause poor performance. The opening and closing mechanisms must respond accurately to pressure changes. If a valve sticks, the system can operate under unsafe conditions. Reports suggest that as much as 20% of valve failures occur due to lack of proper care. It's essential for users to understand their importance in maintaining fluid dynamics and ensuring overall system health.
Overflow valve blocks are essential in many industries. They play a crucial role in managing fluid pressure within hydraulic systems. In manufacturing, for instance, they ensure machinery operates safely. These blocks prevent over-pressurization, which can lead to costly damage. A simple malfunction can halt production. Regular checks are needed to ensure they function correctly.
In the automotive industry, overflow valve blocks control fluid in hydraulic brakes. They ensure the system remains efficient and responsive. If a failure occurs, it can jeopardize safety. It's vital for technicians to understand the signs of wear. Reflections on maintenance practices may highlight areas for improvement.
In construction, these devices protect heavy machinery from pressure surges. They safeguard components like pumps and cylinders. Pressure spikes can happen unexpectedly. It’s easy to overlook these systems until issues arise. Awareness and routine inspections can prevent operational hiccups. Over time, industries must adapt their practices to ensure reliability.
Overflow valve blocks are crucial in hydraulic systems. They prevent pressure build-up by diverting excess fluid. Proper maintenance is vital for efficiency and safety. Research indicates that regular checks can reduce failure risks by 30%. However, many operators overlook these checks. This oversight can lead to leaks or system malfunctions.
Instead of routine maintenance, many wait for signs of problems. This reactive approach often results in costly repairs. Common issues include surge pressure, erratic performance, and sticking valves. Scheduled inspections can catch these problems early. It's recommended to inspect the seals and ensure proper seating regularly. Clean any debris that might obstruct flow.
Operators sometimes miss the importance of fluid cleanliness. Contaminated fluid can lead to wear and damage. Industry reports show that 70% of hydraulic failures are linked to fluid quality. Implementing filtration systems can mitigate these risks. Remember that neglecting maintenance can have serious consequences.
Prioritize regular check-ups and maintain your system's overall health.





